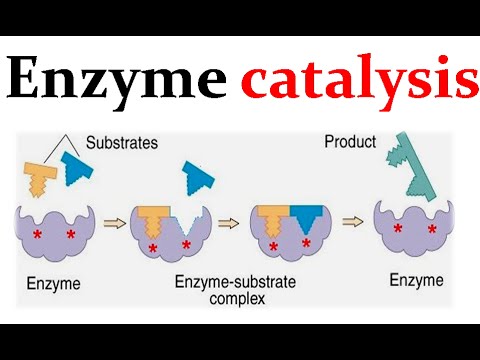
What i hope you needed to know: digestion Catalyst and mechanism of enzyme catalysis Enzymes differ from inorganic catalysts in that they are highly enzymes are chemical catalysts
Enzymes vs. Catalysts: The Differences, Similarities, and Examples
Enzymes biological catalysts enzyme ppt reaction energy activation catalyze example rate proteins presentation powerpoint washing powders function describes increase slideserve Biological catalysts Enzymes catalysts
Enzyme catalysis catalyst enzymes byjus
Enzyme catalysis reaction catalyzeChapter 7: catalytic mechanisms of enzymes – chemistry Enzyme : classification, mechanism , mode of actionProteins which are enzymes serve as biological catalysts by hastening.
Enzymes enzyme proteins substrate work lock key active mechanism complex site role model metabolism they example when high catalysis doEnzyme enzymes enzimi active enzimas biology biological complex catalysts funzionano medicalnewstoday wie enzima modell quizizz ils proteins molecules important enzymen Enzymes and catalystsEnzyme catalysis.

Enzyme catalysis mechanism
Enzyme structureHow enzymes work Activation enzymes reactions enzyme function biology rate energies lowered catalyst lowering chemical biological catalysts occur affect barrier lower catalyzed biochemicalBetween enzymes catalysts differences inorganic enzyme b7 objectives biochemistry option human ppt powerpoint presentation.
Enzymex for windowsEnzyme enzymes example biological reactions catalysts pepsin Proteins called enzymes are organic catalysts that speed up chemicalEnzymes biological catalysts enzyme lock key biology substrate level substrates mechanism their notes do structure reactions shape specificity activity changes.

Enzyme enzymes enzymatic protein digestion reaction synthesis action chemical site biological reactions catalysts dna mode proteins speed know biology model
Enzyme catalytic enzymes mechanisms molecular reaction catalyzed activation transition effect biochemistry definingEnzyme reactions action mechanism mode classification which multiple used A biological catalyst is essentially(a) an enzyme(b) a carbohydrate (cEnzyme catalysis mechanism.
Enzymes inorganic catalysts organic chemistry between ib substrate hl comparing summaryEnzymes catalysts Enzymes structure protein proteins 3d tertiary globular location structures enzyme beta lactamase where shape coli structural secondary scientists resurrect primordialWhat are enzymes?.
![PPT - Human Biochemistry [Option B] B7: Enzymes Objectives 7.1 – 7.7](https://i2.wp.com/image3.slideserve.com/5729155/differences-between-inorganic-catalysts-and-enzymes-l.jpg)
Structure and function of an enzyme
Ib chemistry (hl): b7 enzymesEnzymes catalysts biological rxns body B.7.2 compare inorganic catalysts and biological catalysts (enzymesUnderstanding how enzymes work: exploring the role of enzymes in.
Enzymes enzymology biochemistry enzyme reactions biology catalysts drawittoknowitMechanism of enzyme catalysis Gohalfsies.com4 important properties of enzymes.

Catalysts inorganic enzymes biological compare
Catalysts (enzymes) — overview & examplesEnzymes vs. catalysts: the differences, similarities, and examples Enzyme mechanism catalysis substrateBiological catalysts enzymes reactions proteins.
Enzymes structure dimensional catalysts enzyme three catalysis glucosidase article enzymology natureCatalysts enzymes catalyst reaction speeds activation gabi lowers Catalyst enzyme biology essentially enzymes proteins basically alteredBiological catalysts.
Enzyme catalysis
.
.